2.4.3.3 Numerical example
The Gebhart method describes the radiative heat transfer in terms of heat coming from one surface and absorbed by another, including all reflections. The Gebhart matrix traces exactly the radiative transfer contribution of each surface to the others.
The plates exchange heat with each other and with the room, but only the plate surfaces facing each other are to be considered in the analysis (other side assumed to be perfectly insulated).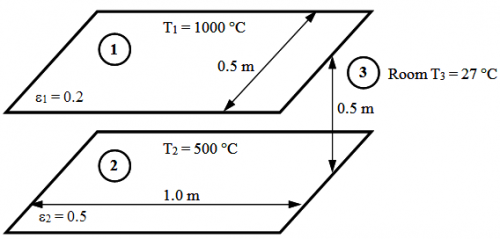
The view-factor of between the two surfaces is analysed to be 0.285. The Gebhart factor for this problem the result would become:
B12 = 0.1473 (very close to the factor if no reflection are taken into account = F12 x ε2 = 0.1425)
In this case the radiative exchange can be calculated by:![]()
The surface to surface heat transfer matrix (in W) of this system is given below for this method.
