Problem 3: Fixed-fixed beam
The equations for all 3 thermal load cases are shown below, the colors represent temperature field (white is high and black is low). The equations give the axial deformation u of the beam, the deflection w of the beam, and the axial stresses in the beam.
 | Boundary Conditions: u (x=0) = 0 w (x=0) = 0 β (x=0) = 0 u (x=L) = 0 w (x=L) = 0 β (x=L) = 0 |
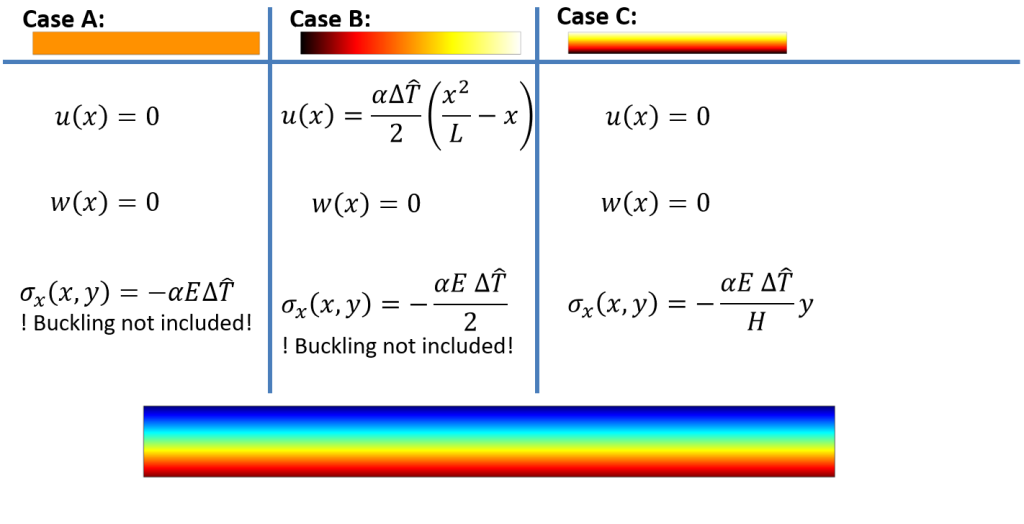
The figure of the deformed beam illustrates the deflection resulting from load case C. Colors represent the axial stress field (green is zero, red is positive and blue is negative). Note that the boundary effects as shown in the figure is not included in the equations!
| Name | Symbol | Units | Description |
| Shear force | D | N | Internal shear force as function of the longitudinal direction (x) |
| Young’s modulus | E | N/m2 | Young’s modulus of the material |
| Axial force | F | N | Internal axial force as function of the longitudinal direction (x) |
| Height | H | m | The total length of the beam |
| Length | L | m | The total length of the beam in longitudinal direction |
| Moment | M | N/m | Internal moment as function of the longitudinal direction (x) |
| Temperature | ΔT | K | The biggest temperature difference in the beam |
| Axial deformation | u | m | Axial deformation of the beam as function of the longitudinal direction (x) |
| Deflection | w | m | Deflection of the beam as function of the longitudinal direction (x) |
| CTE | α | K-1 | Coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of the material |
| Rotation | β | rad | Rotation of the beam as function of the longitudinal direction (x) |
| Axial stress | σx | m | Axial stress of the beam, i.e. combined thermal and mechanical stress, as function of the longitudinal direction and the direction perpendicular (x and y) |
References


This month, the first microcredentials have been awarded to the participants who successfully took part 1 of the course ‘Mechatronics System Design’ by Mechatronics Academy in cooperation with their partner High Tech Institute.
Read more
For 10 years the Gas Bearing Workshop has been the most specific forum for the gas bearing community in the western world.
Read more